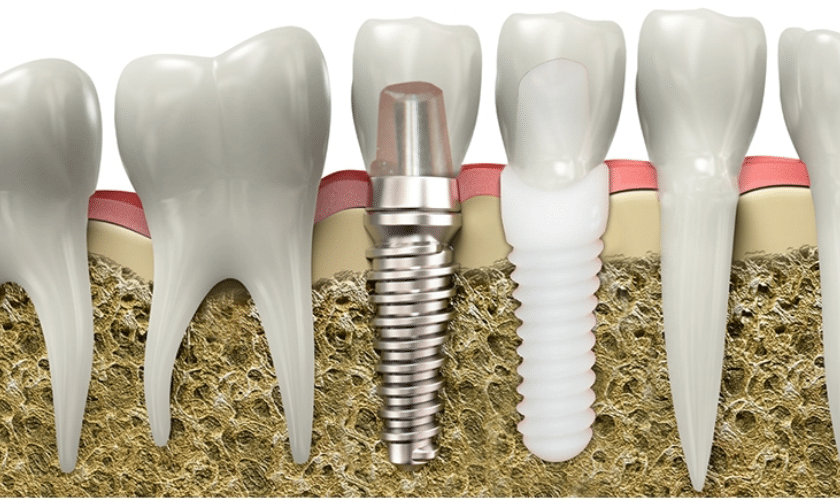
With a growing demand for dental implants, the search for materials balancing functionality, aesthetics, and biocompatibility intensifies. Zirconia, a crystal-clear ceramic, has stepped into the limelight, captivating the dental community with its unique properties and promising outcomes. We will delve into the reasons behind the growing popularity of zirconia implants, compare them with traditional titanium counterparts, and explore real-life success stories that attest to their transformative impact. Join us on a journey through the cutting-edge world of dental technology as we explore everything you need to know about zirconia implants.
The Rise of Zirconia Implants in Dentistry
Zirconia implants emerged in the field of dental implantology as a compelling alternative to traditional titanium implants. This innovative material boasts a toothlike color, exceptional mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and a reduced affinity for plaque. Unlike their metal counterparts, zirconia implants help mitigate issues like apical bone loss and gingival recession, which can lead to the exposure of metal surfaces and a bluish discoloration of the surrounding gingiva (Özkurt, Z., & Kazazoğlu, 2011).
Presently, a predominant number of zirconia implants in production are designed as one-piece implants. There is a compelling notion that zirconia has the potential to improve epithelial attachment during the healing process. The hypothesis stems from the idea that bacterial biofilm tends to accumulate less on zirconia surfaces compared to titanium. Zirconia implants may have a lower risk of inflammation and infection compared to titanium implants. It’s primarily due to the assumption that the soft tissues surrounding them are less prone to such issues (Cionca et al., 2017).
Will Zirconia Implants Replace Titanium Implants?
Zirconia implants boast success rates comparable to titanium implants, offering a superior soft tissue response and reduced material corrosion. Renowned for its exceptional osseointegration capabilities, it has captured the attention of both researchers and clinicians. Serving as a metal-free substitute for titanium implants, zirconia finds its primary application in the anterior esthetic zones.
Not only do these implants exhibit osseointegration on par with their titanium counterparts, but they also showcase an enhanced soft-tissue response. Unlike titanium, zirconia does not corrode, and its resistance to bacterial adhesion sets it apart. Introduced in Europe in the early 2000s, the popularity of zirconia implants in the USA soared post-FDA approval in 2011. Patients are proactively exploring diverse implant choices, prompting them to approach dental offices with requests for alternatives to conventional titanium implants (Webber et al., 2021).
Innovations in Zirconia Implant Technology
In the realm of implant dentistry, nanotechnology has ushered in a groundbreaking era, particularly in titanium implants. It is gradually making strides in the realm of ceramic implants. The application of nanoscale modifications to zirconia. It is a key component in ceramic implants, witnessing two notable trends – surface patterning and the application of innovative ceramic coatings.
This surge of interest and the swift pace of technological advancement are driving the evolution of zirconia surface modification to nano texturization levels. The remarkable outcome of this progress is the ability to prompt bone formation in a surprisingly brief period, achieving significant results in less than a month. This transformative journey in dental implant technology showcases the immense potential of nanotechnology to reshape and enhance the field. As a result, it creates a promising future where implant procedures are not only efficient but also remarkably accelerated (Gupta et al., 2020).
Advantages of Zirconia Implants
One notable advantage of opting for zirconia implants is their ability to eliminate the aforementioned complications, addressing the aesthetic concerns of patients who prefer a metal-free implant solution. Beyond aesthetics, zirconia also stands out for its impressive combination of high strength, fracture toughness, and biocompatibility. This makes it a sought-after choice in dental implant procedures, offering patients a reliable and aesthetically pleasing option for tooth replacement (Cionca et al., 2017).
Zirconia’s heightened visual appeal stems from its remarkable capability to conceal dark substrates effectively. It has excellent opacity across both the visible and infrared spectrums while maintaining controlled translucency. Similarly, the surface of titanium-based implants, such as zirconia implants, undergoes a transformative process to enhance their biological compatibility. Common techniques include sandblasting, acid etching, and the selective infiltration technique.
This method entails coating the surface with glass infiltration, subjecting it to temperatures surpassing the glass transition threshold. It subsequently facilitates the infusion of molten glass between the material grains. This intricate process not only elevates the aesthetic qualities of zirconia but also improves the biological responses of titanium implants. It eventually marks a significant advancement in dental and medical applications (Webber et al., 2021).
As we traverse the various facets of zirconia implants in this guide, one thing becomes abundantly clear – we stand at the precipice of a new era in tooth replacement technology. The journey through zirconia’s triumphs and the insightful perspectives leaves us with a profound appreciation for the strides made in dental science. As we look to the future, with ongoing research and innovations, zirconia implants are poised to redefine not only the technical aspects of dental implants but also the overall patient experience. The potential for healthier, more natural-looking smiles has never been more promising. Zirconia implants, with their remarkable blend of strength, beauty, and safety, beckon a new era in dentistry.
Reference List
– Özkurt, Z., & Kazazoğlu, E. (2011). Zirconia dental implants: a literature review. Journal of Oral Implantology, 37(3), 367-376.
– Cionca, N., Hashim, D., & Mombelli, A. (2017). Zirconia dental implants: where are we now, and where are we heading?. Periodontology 2000, 73(1), 241-258.
– Webber, L. P., Chan, H. L., & Wang, H. L. (2021). Will zirconia implants replace titanium implants?. Applied Sciences, 11(15), 6776.
– Gupta, S., Noumbissi, S., & Kunrath, M. F. (2020). Nano modified zirconia dental implants: Advances and the frontiers for rapid osseointegration. Medical Devices & Sensors, 3(3), e10076.